题目
已知 f(x)= ) ((cos x))^(x^-2), xneq 0 a, x=0 . 在 x=0 处连续,则 a= __ _.
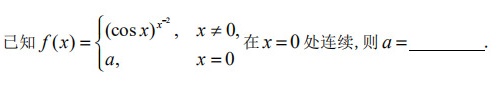
题目解答
答案
解析:
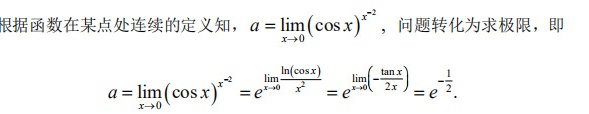
解析
步骤 1:确定函数在 x=0 处连续的条件
函数 f(x) 在 x=0 处连续,意味着 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}f(x)=f(0)$。根据题目中给出的函数定义,当 x=0 时,f(0)=a。因此,我们需要求出 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}f(x)$,并令其等于 a。
步骤 2:求解极限 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}{(\cos x)}^{{x}^{-2}}$
为了求解这个极限,我们首先将指数函数转换为自然对数的形式,即 ${(\cos x)}^{{x}^{-2}}={e}^{{x}^{-2}\ln (\cos x)}$。接下来,我们需要求解 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}{x}^{-2}\ln (\cos x)$。
步骤 3:应用洛必达法则求解极限
由于 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}{x}^{-2}\ln (\cos x)$ 是一个不定型的极限,我们可以应用洛必达法则。首先,将极限转换为 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {\ln (\cos x)}{x^2}$。然后,应用洛必达法则,求导分子和分母,得到 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {-\sin x}{2x\cos x}$。再次应用洛必达法则,得到 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {-\cos x}{2\cos x-2x\sin x}$。最后,将 x=0 代入,得到 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {-\cos x}{2\cos x-2x\sin x}=-\dfrac {1}{2}$。
步骤 4:求解 a 的值
根据步骤 2 和步骤 3 的结果,我们得到 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}{(\cos x)}^{{x}^{-2}}={e}^{-\dfrac {1}{2}}$。因此,a 的值为 ${e}^{-\dfrac {1}{2}}$。
函数 f(x) 在 x=0 处连续,意味着 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}f(x)=f(0)$。根据题目中给出的函数定义,当 x=0 时,f(0)=a。因此,我们需要求出 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}f(x)$,并令其等于 a。
步骤 2:求解极限 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}{(\cos x)}^{{x}^{-2}}$
为了求解这个极限,我们首先将指数函数转换为自然对数的形式,即 ${(\cos x)}^{{x}^{-2}}={e}^{{x}^{-2}\ln (\cos x)}$。接下来,我们需要求解 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}{x}^{-2}\ln (\cos x)$。
步骤 3:应用洛必达法则求解极限
由于 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}{x}^{-2}\ln (\cos x)$ 是一个不定型的极限,我们可以应用洛必达法则。首先,将极限转换为 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {\ln (\cos x)}{x^2}$。然后,应用洛必达法则,求导分子和分母,得到 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {-\sin x}{2x\cos x}$。再次应用洛必达法则,得到 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {-\cos x}{2\cos x-2x\sin x}$。最后,将 x=0 代入,得到 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {-\cos x}{2\cos x-2x\sin x}=-\dfrac {1}{2}$。
步骤 4:求解 a 的值
根据步骤 2 和步骤 3 的结果,我们得到 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}{(\cos x)}^{{x}^{-2}}={e}^{-\dfrac {1}{2}}$。因此,a 的值为 ${e}^{-\dfrac {1}{2}}$。