题目
lim _(xarrow 1)(e)^dfrac (1{x-1)}=
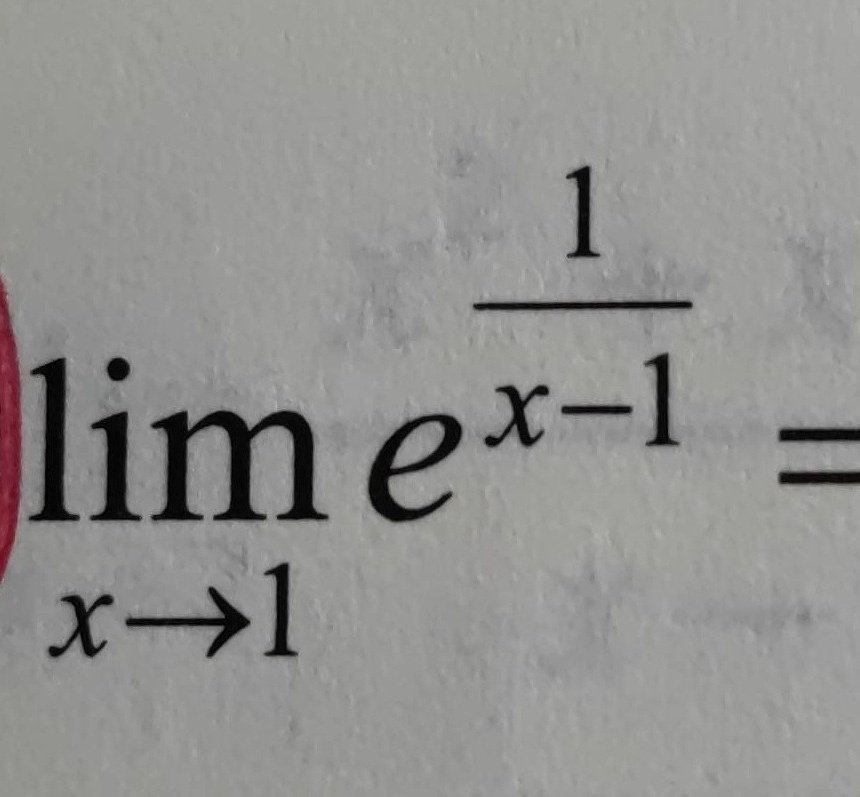
题目解答
答案

解析
本题考查极限的左右极限计算,特别是涉及指数函数与分式结合的未定式。解题核心在于:
- 分情况讨论当$x$从右侧趋近于1($x \to 1^+$)和左侧趋近于1($x \to 1^-$)时,表达式的行为;
- 处理未定式$0 \cdot (-\infty)$时,通过变量代换和等价无穷小分析极限值;
- 判断极限是否存在:若左右极限不相等,则原极限不存在。
当$x \to 1^+$时
- 变量代换:令$t = x - 1$,则$t \to 0^+$;
- 表达式变形:
$e^{\dfrac{1}{x-1}} \cdot \dfrac{1}{x-1} = e^{\dfrac{1}{t}} \cdot \dfrac{1}{t}$ - 分析趋势:
- $\dfrac{1}{t} \to +\infty$;
- $e^{\dfrac{1}{t}} \to +\infty$;
- 乘积结果:$+\infty \cdot +\infty = +\infty$;
- 结论:
$\lim_{x \to 1^+} e^{\dfrac{1}{x-1}} \cdot \dfrac{1}{x-1} = +\infty$
当$x \to 1^-$时
- 变量代换:令$t = x - 1$,则$t \to 0^-$;
- 表达式变形:
$e^{\dfrac{1}{x-1}} \cdot \dfrac{1}{x-1} = e^{\dfrac{1}{t}} \cdot \dfrac{1}{t}$ - 分析趋势:
- $\dfrac{1}{t} \to -\infty$;
- $e^{\dfrac{1}{t}} = e^{-\infty} \to 0$;
- 未定式:$0 \cdot (-\infty)$;
- 等价无穷小分析:
令$s = -t$($s \to 0^+$),则表达式变为:
$e^{-\dfrac{1}{s}} \cdot \left(-\dfrac{1}{s}\right) = -\dfrac{e^{-\dfrac{1}{s}}}{s}$- $e^{-\dfrac{1}{s}}$衰减速度远快于$\dfrac{1}{s}$增长;
- 极限值:$\lim_{s \to 0^+} -\dfrac{e^{-\dfrac{1}{s}}}{s} = 0$;
- 结论:
$\lim_{x \to 1^-} e^{\dfrac{1}{x-1}} \cdot \dfrac{1}{x-1} = 0$
综合判断
- 左极限为0,右极限为$+\infty$;
- 左右极限不相等,因此原极限不存在。